Electric Field Intensity Due to a Dipole
Electric Field Intensity Due to a Dipole: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Field Due to Dipole at Axial Point, Electric Field Due Dipole at Equatorial Point & Electric Field Due Dipole at General Point etc.
Important Questions on Electric Field Intensity Due to a Dipole
Electric field on the axis of a small electric dipole at a distance is and at a distance of on a line of perpendicular bisector. Then
Consider two spheres of the same radius having uniformly distributed volume charge density of same magnitude but opposite sign and The spheres overlap such that the vector joining the centres of the negative sphere to that of the positive sphere is The magnitude of the electric field at a point outside the spheres at a distance in a direction making an angle with is found to be The value of is (Distance is measured with respect to the mid point of the line joining the centers of the two spheres.)
Electric field due to the electric dipole at the equatorial plane is given as:
The electric field at due to a dipole of dipole moment is perpendicular to , then the angle is equal to
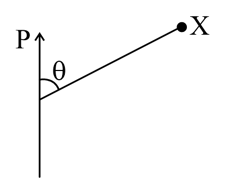
A given charge is situated at a certain distance from an electric dipole in the axial position experiences a force If the distance of the charge is doubled, the force acting on the charge will be : -
The magnitude of electric field intensity at point due to a dipole of dipole moment, kept at origin is :
What is the angle between the electric dipole moment and the electric field strength due to it on the equatorial line?
Electric field of a dipole at a distance is proportional to :-
The electric field due to an electric dipole at a distance from its centre in axial position is . If the dipole is rotated through an angle of about its perpendicular axis, the electric field at the same point will be
A given charge is situated at a certain distance from an electric dipole in the end-on position experiences a force . If the distance of the charge is doubled, the force acting on the charge will be :-
Two electric dipoles of moment and are placed in opposite direction on a line at a distance of . The electric field will be zero at point between the dipoles whose distance from the dipole of moment is :-
Electric field at a far away distance on the axis of dipole is What is the electric field at a distance on perpendicular bisector?
A dipole of dipole moment is kept at the center of a ring of radius and charge The dipole moment has direction along the axis of the ring. The resultant force on the ring due to the dipole is:
For the same distance from centre of the dipole the ratio of electric fields at longitudinal and transverse position is
Two point charges of and separated by a distance of practically form an electric dipole. Calculate the electric field at point which is at a distance of from the midpoint and on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the two charges.
Two charges and placed apart essentially form an electric dipole. What will be the electric field at point on the axis of the dipole which is away from its centre on the side of the positive charge?
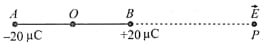
For the dipole, is given, what would be the electric potential at A:
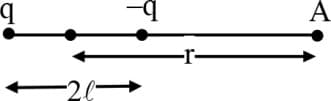
Charges and located at and respectively with on X-axis constitute an electric dipole. ( origin) is the mid-point of the dipole and is a point on perpendicular bisector (Y-axis). A charge experiences an electrostatic force when placed at where and If is now moved along the equatorial line to such that experiences force What is the value of (consider )
A dipole is placed at origin of co-ordinate system as shown in figure. What will be the electric field at point ?
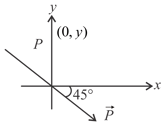
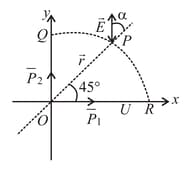
For a system of two dipoles and as shown in the figure (both are at origin and perpendicular to each other along and -axes, respectively) and ) denotes magnitude of and is quite large in comparison to dimensions of dipoles, is resultant electric field and is a quarter of circle whose centre is at ).
